ClassicColumns / Analysis, Decision making process, Mohamed Ogbi, Proimpact, Proimpact Marketing Consultancy, Sony / April 9, 2015
Sony’s decision making process
Sony had reported a loss for three years from 2009 until 2012 when company announced the restructuring of its management to try to set an alternative approach for the future.
Sony Corporation is a leading Japanese company, known as one the most influential leading manufacturer of consumer electronics, entertainment and game products. Sony had reported a loss for three years from 2009 until 2012 when company announced the restructuring of its management to try to set an alternative approach for the future. In this study, I review the decision making process of Sony and conduct porter’s five forces of analysis and time series forecast using three models: moving averages, weighted moving average and exponential smoothing averages.
Elements of Sony’s decision making process
The problem finding
Sony has suffered a loss in the past three years both on the profit and corporation value. In addition, as many organisations suffer from being usually reactive in term of finding predetermine future problems and prepare for them, in addition to that Sony had, done the same. The management did not take actions proactively and because of that, Sony was suffering loss since 2009 until finally Sony decided to bring a new management with a new leadership to try to develop a new business strategy in respect to the global changes in consumer electronics industry. With the new leadership of Mr Hirai, who was the head of Sony computer entertainment in japan and later in as the head of Sony’s international business affairs in New York.
Sony Swot Analysis

Problem solving and outcome
As Mr. Hirai, working at the centre of management team that will connect and work with all the heads of each business by restructuring the management of each business and making some organisational changes. By reading some of Sony’s news releases in 2012, by the time Mr. Hirai arrived he already decided to work and set new performance objective for each business group, the new business management can focus on its structure can focus on its goals, define their mission, knowing what the priorities of their department are and focus on S.M.A.R.T goals.
In addition to that, Mr. Hirai already made some changes and gave each manager a clear goal. For instance:
Corporate Executive officer Masaru Kato and Tadashi Saito (chief strategy officer) will oversee the Sony’s group overall financial management, corporate business strategies and technology strategy.
Mr. Suzuki (corporate executive officer and EVP) will oversee product strategy.
From Sony’s annual report, we can see that the new management had decided to stop loss and change that into profit. On the other hand, decreasing Sony’s liabilities by selling assets, decreasing operating costs, layoffs reached 10,000 jobs and cut its TV production for about 50%, and that’s all to try to get its consumer electronics division down to smaller, more manageable and profitable operation, but even after these changes they still suffer a loss in electronics department. In fact, Sony only made money through selling life insurance, selling its corporate headquarters in Tokyo and sold its corporate headquarter in New York City, which is sold for a billion us dollars, without that, it would not be reporting profit in 2013. On the other hand, Sony seems optimistic about next year sales strategy, especially after the announcement of play station 4, but is, that when it comes to head to head competition with Apple and Samsung, Sony is still not making much of a head.
For example, Apple had long formed long-term relationships with Micron, Intel and Samsung. Since Mid-2007, apple has commanded about 25% of global flash production, because apple is buying these components in large quantities that it can exercise a significance advantage over suppliers. This enables Apple to negotiate better terms of quality and prices. Second, by commanding such a large quantity of the global market, apple had created new barriers to entry or even difficulties for its competitors such as Sony, because they can buy the components in limited quantities and with a higher price.
On the other hand, Mr. Hirai answered on an interview when he was asked by a BBC reporter about if Sony is better than Apple and Samsung. And he answered “We are in so many different product categories… for example, we have a leadership position in video game space with PS4 coming up this year….that’s an area that Samsung is not in… we are very strong in our entertainment properties, and financial services…. Entertainment Samsung is not in…”
Strategic recommendations
Based on our method of analysis, the most challenging factors for Sony are Macroeconomic risks, including (economic downturn and currency) and competition. According to that, I suggest these recommendations.
Segment focus:
Since the establishment of Sony in 1946, the company has expanded into different business segments such as Electronics, Movies, Music, Game and financial services. While the number of production lines increased, the more liability the company has in terms of customer service, marketing and R&D. facing competitors who are specialized within each segment. Therefore, leaders of Sony should focus on segments they know they are better than others at or focus on products that are not provided by other competitors, for example, Game, insurance and financial services.
Acquiring aggressively
Once the company decided to focus on certain segments, it should start to acquire aggressively within these segments. That will increase Sony’s market share, to have economies of scale, access to new technologies and reduce costs. The higher the market share, the more Sony’s influence increase over prices.
Financial recommendations
- Sony must insure stable cash flows to be able to avoid liquidity problems and focus on increasing sales.
- The increasing reliance on global consumer demand causes to increase in their operation sensitivity to exchange rates and to the global economy. They should find new financial strategies to avoid Macroeconomic risks
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis of Sony Corporation
- The threat of new entry (Low)
A huge amount of capital needed for a new company to enter the consumer electronics industry. Innovation and high scale economy are other barriers that make it difficult for new companies to enter, not to forget about the ability to work with different products in order to compete. Moreover, policies and government regulations are another barrier to enter.
- Product differentiation: even though, Sony’s value and ranking went down from being N.40 (with value of 9,111 $m) in best global brands list 2012 to N.46 (with a value of 8,408$m) 2013, it still indicates a strong brand image. This would not happen without constant innovation, ability to change and a strong base of loyal customers. A new entrant will need to create a brand image in order to compete, but still very costly.
- Capital requirements: Machinery, professional human resources, high tech production and research & production requires a huge amount of capital, because a new entrant will not only need to spend on existing technology, but also to indicate market trends. Furthermore, try to work on a much more advanced technology than the present one in order to be ready to enter and keep up with other competitors.
- Economies of scale: the strong brand of Sony and physical resources Such as property and intangible assets are significant, and for a new company to enter, it has to solve difficulties in procurement, research & development and marketing costs.
- Distribution channels: Sony has a large global distribution network, which gives it the ability to reach its worldwide network of customers.
- Government policies: due to the need of government approvals, the process itself might be a barrier, because of the different policies from one country to another, which might also consume time and resources
- Threat of Substitutes (Low): the wide range of products, left most of other substitutes either not efficient or outdated. However, they are still competing with Apple and Microsoft in term of gaming and apps software. Apple had introduced a variety of games on their products iPhone and iPad with the ability to choose and download apps and games immediately from App store, which was a substitute for Sony’s play station hardware. In this Sony has introduced Xperia for mobile gaming and changed play station hardware to make it more as a computer to be able to download and add software to it, but still targeting to develop a gaming network that can compete with Apple App store. In addition, by that, Sony decided to outsource the service to Gaikai.Inc, which is a US based developer that provides interactive cloud based gaming service. According to Sony’s annual report 2013, the company will establish a new platform that provides play station 4 customers the ability to broadcast their gameplay in real time, exchange information on content to social networks services and offer a new entertainment to gamers.
- Bargaining power of buyers (High): the information technology and the internet gave the buyer a high bargaining power, since the access to product information and prices is possible, which gives them the ability to compare quality and prices between different companies.
- Bargaining power of suppliers (Low): Sony is a big corporation with large and different demands of suppliers, which makes it difficult to know the power of the supplier, because the supply network is large. However, suppliers are relatively smaller than Sony and by that have a weak bargaining power over Sony. Sony has an advantage of negotiating of negotiating directly with suppliers due to the large demand, and it obtains high quality products in low prices.
- Intensity of Rivalry (High): rivalry is high due to intense competition and high exit costs. The completion is also difficult because, it is hard to keep up with the major factors that affect companies in the global consumer electronics industry such as continues research and development, innovation, price, quality, brand image, services and marketing. In addition, the short product life cycle and the need to develop new products are other issues that Sony Corporation always need to work on, especially when you have this high competitive environment; the growth rate is slow and thus increase the intensity of the competition.
Time series forecasting
1. Moving average method
| Year | Sales | Moving Total | Moving Average |
| 2009 | JPY 7.70 | ||
| 2010 | JPY 7.20 | ||
| 2011 | JPY 7.18 | ||
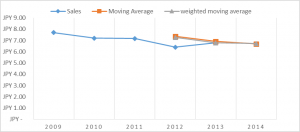
| 2012 | JPY 6.40 | JPY 22.08 | JPY 7.36 |
| 2013 | JPY 6.80 | JPY 20.78 | JPY 6.92 |
| 2014 | JPY 20.38 | JPY 6.70 |
2. Weighted moving average
| Year | Sales | weighted moving average |
| 2009 | JPY 7.70 | |
| 2010 | JPY 7.20 | |
| 2011 | JPY 7.18 | |
| 2012 | JPY 6.40 | JPY 7.27 |
| 2013 | JPY 6.80 | JPY 6.79 |
| 2014 | JPY 6.73 |
Graph indicating sales, moving average and weighted moving average
3. Exponential smoothing using 0.9 as the value of α
| Year | Sales | Exponential smoothing |
| 2009 | JPY 7.70 | |
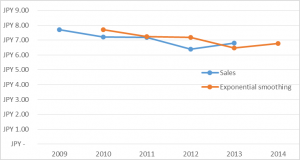
| 2010 | JPY 7.20 | JPY 7.70 |
| 2011 | JPY 7.18 | JPY 7.25 |
| 2012 | JPY 6.40 | JPY 7.19 |
| 2013 | JPY 6.80 | JPY 6.48 |
| 2014 | JPY 6.77 |
Exponential smoothing and sales
Conclusion
Sony’s decision making and strategies have been analysed by using Porter’s five forces analysis and time series forecasting. These tools gave us some information about the internal and external factors of Sony’s business environment. By understanding those tools, we can find company’s competitive advantages to retain market shares both in developed and emerging markets, but we need to take into consideration that forecast change for the future. In this way, the company can adjust its strategy to changes in the environment in which it operates.
References
- Anonymous. 2014. [online] Available at: http://www.personaglobal.com/admin/material/facts/contents/(IDM)InnovativeDecisionMaking.pdf [Accessed: 15 Mar 2014].
- Barua, P. 2014. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis of Sony Corporation. [online] Available at: http://www.scribd.com/doc/71044451/Porter-s-Five-Forces-Analysis-of-Sony-Corporation [Accessed: 17 Mar 2014].
- Boks, C. and Stevels, A. 2003. Theory and practice of environmental benchmarking in a major consumer electronics company. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 10 (2), pp. 120–135.
- FernStrategy | Strategy Development for Technology Firms. 2014. Apple and Industry Forces. [online] Available at: http://fernstrategy.com/2011/02/17/apple-and-industry-forces/ [Accessed: 20 Mar 2014].
- Interbrand.com. 2014. Interbrand – Best Global Brands 2013 – (Brand View). [online] Available at: http://www.interbrand.com/en/best-global-brands/2013/Best-Global-Brands-2013-Brand-View.aspx [Accessed: 20 Mar 2014].
- Sony.com. 2014. Kazuo Hirai. [online] Available at: http://www.sony.com/SCA/who-we-are/leadershipteam/kazuo-hirai.shtml [Accessed: 20 Mar 2014].
- Sony.net. 2014. [online] Available at: http://www.sony.net/SonyInfo/IR/financial/ar/2013/shr/pdf/AnnualReport_E.pdf [Accessed: 21 Mar 2014].
- Sony.net. 2014. Sony Global – News Releases – Sony Establishes New Management Structure. [online] Available at: http://www.sony.net/SonyInfo/News/Press/201203/12-043E/ [Accessed: 18 Mar 2014].
- The Economist. 2014. Stringer theory. [online] Available at: http://www.economist.com/node/18745381 [Accessed: 20 Mar 2014].
- Whitman, T. 2014. Process of Decisions: Learn Decision Making Processes as Implemented by Sony, CWIIL and Virgin. [online] Available at: http://processofdecision.blogspot.it/2012/05/decision-making-process-sony-cwiil.html [Accessed: 20 Mar 2014].
- Wikinvest.com. 2014. Stock:Sony (SNE). [online] Available at: http://www.wikinvest.com/stock/Sony_(SNE) [Accessed: 20 Mar 2014].
- YouTube. 2014. Sony CEO on Microsoft’s Nokia purchase. [online] Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zyjzhpa0jLw [Accessed: 20 Mar 2014].